Ideally, your connectors perform to their rated lifecycles. If you install a connector rated for 10,000 mating cycles, you expect it to go that distance. But if you’ve ever had a cell phone charger stop working correctly, you know that’s not always the case. And for industrial machinery, improper designs and other factors can cause connectors to fail prematurely, which can cause costly machine damage. Here’s a look at some common causes of failure and how to prevent them.
Wear and tear — Like the example above, repeated connection and disconnection of a connector can cause the metal on the contacts to wear and corrode if exposed to water, dust, dirt and other harsh elements. As a result, the mating pins may not properly engage when inserted into the connector shell. Always choose connectors rated for the required mating cycles you will need.
Improper selection — Environments where there may be moisture ingress require special connectors. If a standard connector is used in place of one with an IP68 or IP69 rating or a hermetic design, water can cause the connector to fail. Choosing an undersized connector can also reduce efficiency, thus making the connector work harder to keep up with demand. This will decrease connector life.
Extreme temperatures — If connectors are not rated for extremely high or low temperatures, they will eventually fail. If not rated for high temperatures, the insulation fails and conductivity will also spike. If operated at continued high temperatures, these spikes will add to the temperature elevation, which can cause corrosion and eventually, reduced contact force. This can impact the electrical signal traveling through the connector and cable assembly, which in turn can create an open circuit.
While cold temperatures do not impact connectors as harshly as hot temperatures do, low-temperature designs should be considered if you know your application will require them. Exposure to continued low-temperatures can cause tin-plated connector materials to soften, which in turn increases contact resistance. In addition, cold temperatures can impact other parts of the connector, like making plastic shells go brittle.
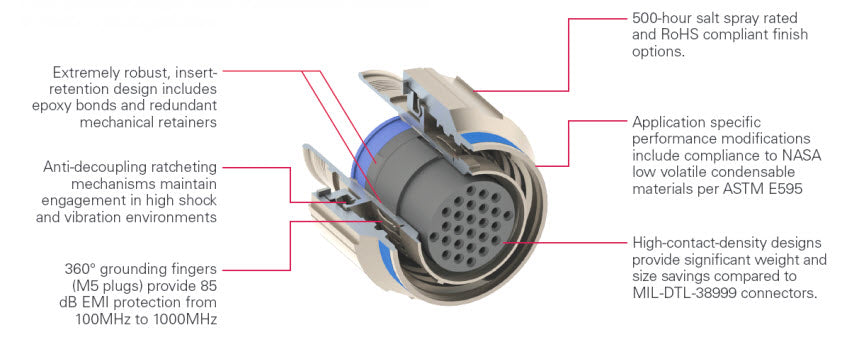
Improper design and installation — If an application will experience shock, vibration and other damaging motions, it is important to find secure designs that create a strong latch. If not securely mounted, the connector contacts, the mating shells and even the cable could suffer damage. In addition, connector and cable assemblies must have proper strain relief and installation routing — using guided troughs, cable carriers and cable glands help to ensure rated assembly life.


